International microwave leakage standard
Microwave leakage standard-When the microwave device is in operation, a part of the microwave leakage occurs. When the leakage standard is greater than a certain value, and the operator is close to the microwave device less than a certain distance, it will have an impact on the human body. Therefore, when we choose microwave equipment, we must pay attention to whether it can be used safely. Today we will look at the international standards for microwave leakage, so that we can purchase microwave equipment in the future.
In order to protect the health of users, the International Electrotechnical Commission and relevant departments of China stipulate that the microwave leakage measured at 5 cm outside the door of the microwave equipment shall not exceed 5 mW/cm2.
However, the standards for microwave leakage in major countries in the world are not very uniform. For example, the microwave leakage standards developed by Europe and the United States and the former Soviet Union differ by 1-2 orders of magnitude. This result may reflect their debate on the effects of microwaves on humans.

Microwave leakage detector
The basic idea of the theory of microwave radiation intensity safety standards developed by the United States is proposed by Schwan.
The basic idea of the theory of microwave radiation intensity safety standards developed by the United States is proposed by Schwan.
1. The effect of microwave on the human body is mainly the thermal effect of microwaves;
2. When the radiation of the microwave to the human body is less than 10 mW/cm2, the operator does not cause various discomforts due to radiation.
After years of practice, the National Institute of Standards (ANSI) in 1982 issued a new microwave radiation safety standard (f/300mW/cm2). It is based on the principle that the body tissue absorption ratio (SAR) value of 0.4 W/kg is never exceeded. Countries such as Canada, the United Kingdom, France and Australia use this standard internationally.
The views of the former Soviet Union on the establishment of microwave radiation intensity standards are:
It is based on the critical strength of animal central nervous system and cardiovascular system dysfunction in animal experiments, and the intensity of clinical symptoms in long-term exposure to microwaves that may leak microwaves. Its starting point is completely different from that of the United States. It belongs to the standard based on the non-thermal effect of microwave. It focuses on the effects of non-thermal effects of microwave on the vegetative nervous system activity of animal body. Countries that use this standard internationally have countries such as Poland, the Czech Republic, and Bulgaria.
However, China’s microwave radiation research work started late, basically based on international research and implementation. In 1979, the Ministry of Health promulgated the “Temporary Health Standard for Microwave Radiation.” The standard specifies that the intensity of the microwave radiation is 50 μW/cm 2 (calculated as 6 hours per day). If the time limit is exceeded, the maximum allowable amount per day is 300 μW/cm 2 , and the maximum allowable amount per day is not more than 5 μW/cm 2 . The revised standard in 1983 was: the intensity of the microwave radiation did not change, but the daily exposure time was changed to 8 hours, that is, the maximum allowable amount was 400 μW/cm 2 . At the same time, it is treated differently according to the following conditions:
Considering the biological effect of microwave, the maximum allowable amount of pulse wave is 250 μW/cm 2 ;
In some types of work, only the limbs are exposed to microwave radiation, and the maximum allowable dose per day is 10 times larger than the whole body radiation dose compared with the case where the whole body is exposed to microwave radiation;
Compared with fixed-field microwave radiation, non-fixed-direction microwave radiation (such as microwave radiation from a rotating antenna) can be twice as large as the fixed condition under the same conditions;
Under normal circumstances (referring to non-accident conditions), the human body can withstand the above-mentioned microwave radiation dose. The human body has a thermal regulation function, so that the portion irradiated by the microwave does not excessively accumulate heat to reach the point of being injured.
On the other hand, from the perspective of ensuring the safety of equipment, it is an important technical indicator to suppress microwave leakage in the design and manufacture of microwave equipment. We should take safety measures to control microwave leakage as much as possible. For example, a furnace door interlocking device is used; a microwave leakage energy suppressor is installed at the inlet and outlet of a continuous-transport industrial microwave device to minimize microwave leakage. At present, the amount of microwave leakage in domestic cooking microwave ovens or industrial microwave equipment is: 5cm away from the equipment, microwave leakage power ≤5mW/cm2 (2450MHz) and microwave power ≤1mW/cm2 (915MHz).
Attachment: Relevant rules formulated by the International Industrial Microwave Research Committee.
Table 1:Exposure Limit Values
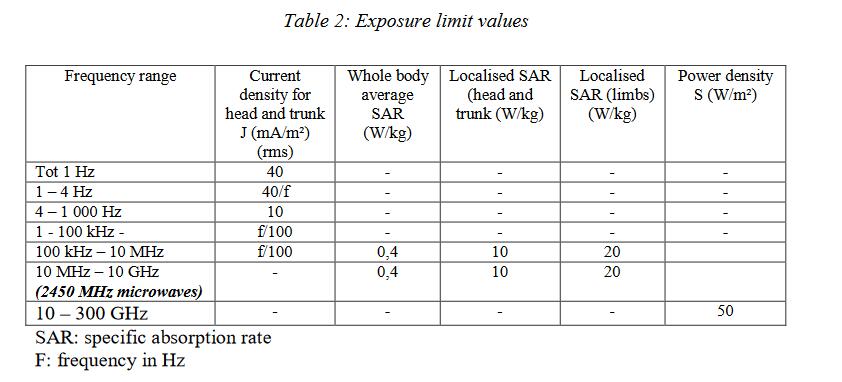
Table 2:Action Values
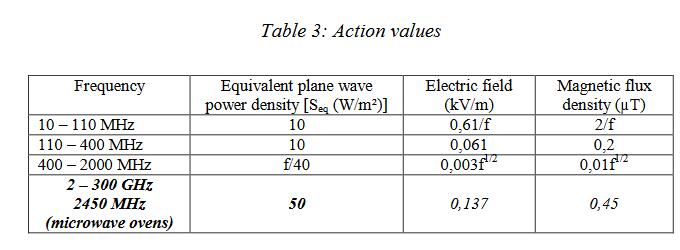
Related Items



